Metaphysics is a foundational branch of philosophy that delves into profound questions about the nature of reality, the structure of the universe, and the relationship between the physical and the non-physical. It encompasses areas like ontology, cosmology, and the philosophy of mind, providing a deeper understanding of the fundamental aspects of existence and our place in the universe. See my discussion post where I share some of my cursory thoughts and opinions on the subject.
Definition and Nature of Reality
In this aspect of metaphysics, philosophers explore what it means for something to exist and what constitutes reality. They question whether reality is solely composed of physical entities or if there are non-physical aspects to it, such as abstract objects or ideas.
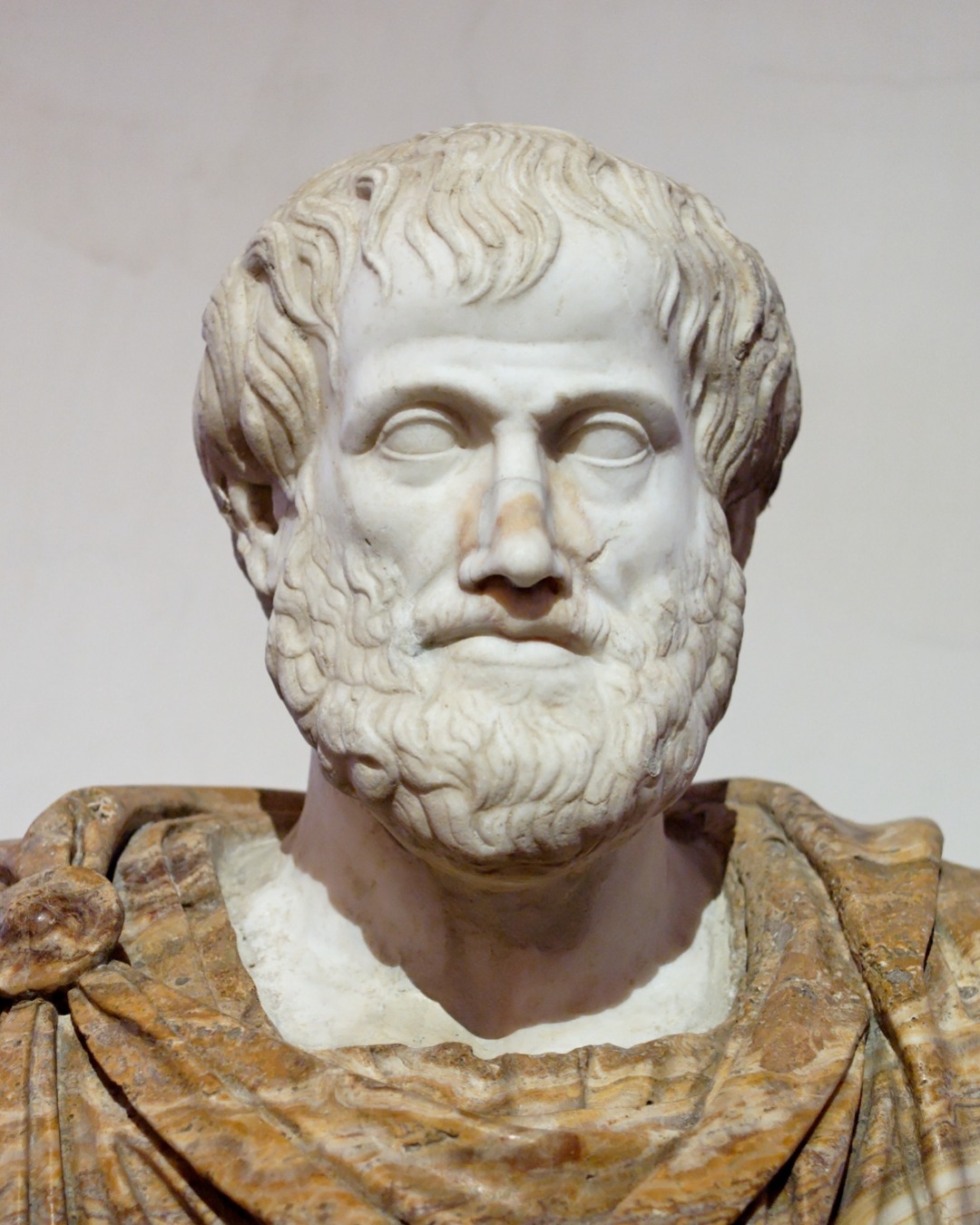

Aristotle introduced the concept of hylomorphism, which posits that everything in the physical world is composed of both matter (hyle) and form (morphe). This theory became a foundational idea in metaphysics, shaping discussions about the nature of reality, substance, and change.
Ontology: The Study of Being and Existence
Ontology focuses on the study of being and existence. It examines the various categories of entities that exist and investigates their properties and relationships. Philosophers in this area ponder questions like:
- What kinds of things exist?
- Are there universals that exist beyond individual instances of things?
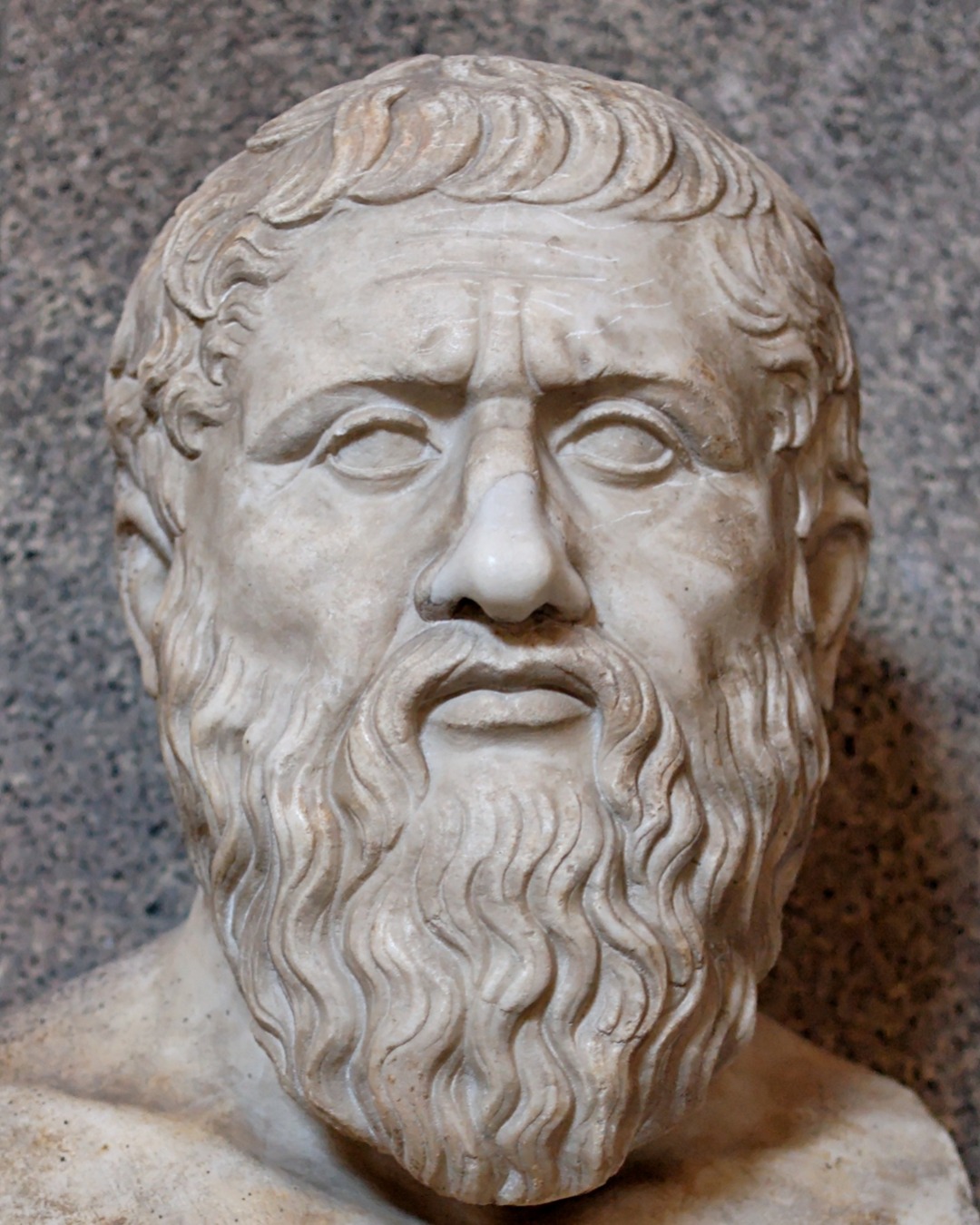

Plato’s Theory of Forms postulates that abstract, ideal forms exist as true reality, and physical objects are imperfect copies. This deeply influenced later metaphysical discussions about universals, abstract objects, and the nature of reality.
Cosmology: The Study of the Universe and its Origin
Cosmology in metaphysics deals with the study of the universe as a whole, including its origin, structure, and development. Philosophers ponder the nature of time, space, and causality, and they explore theories about how the universe came into being and how it might evolve.
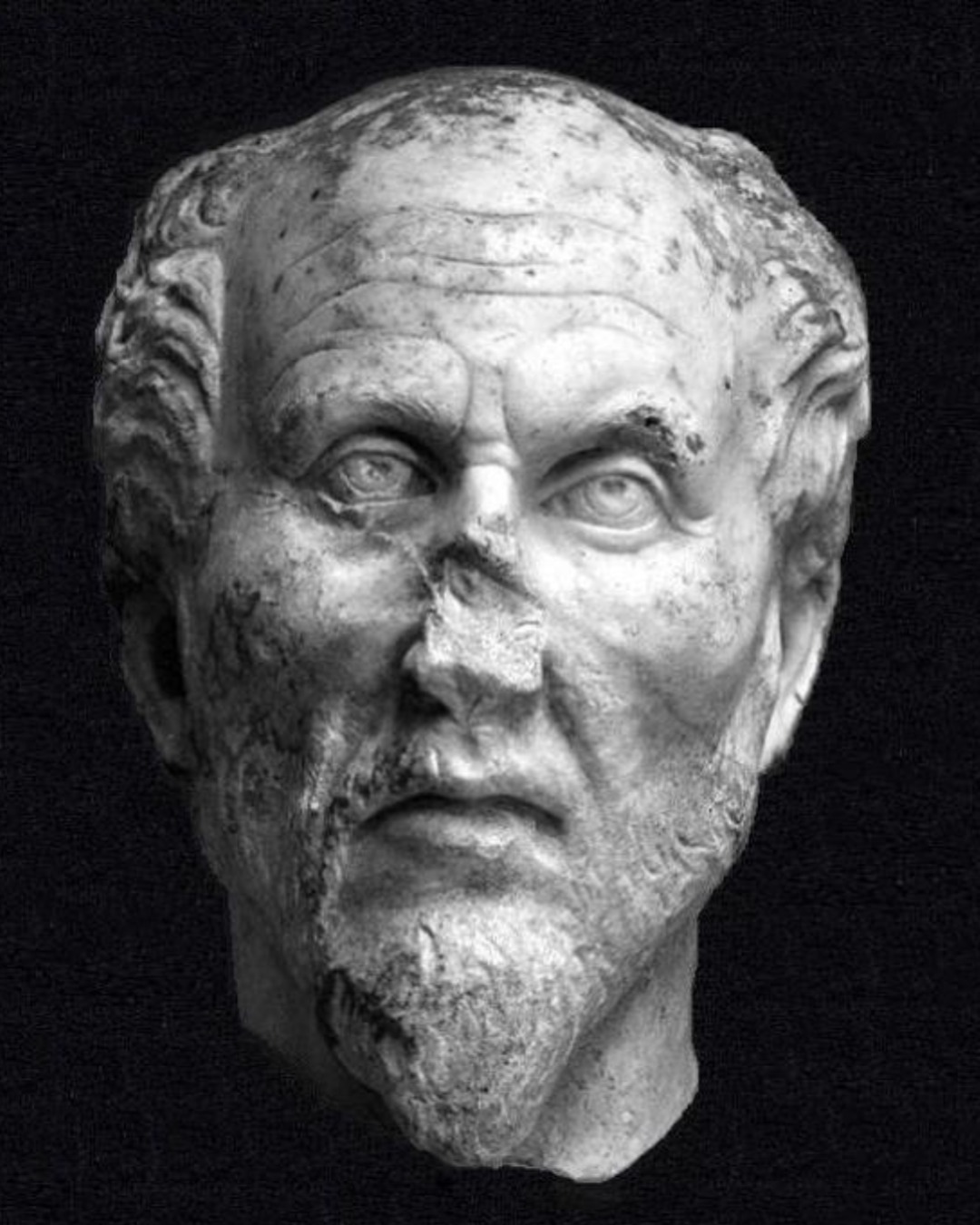

Plotinus is known for founding Neoplatonism which emphasized the existence of a transcendent One, the emanation of reality from this One into multiple levels of existence, and the return of the soul to the One through philosophical contemplation.
Epistemology: The Study of Knowledge and its Nature
While epistemology is traditionally considered a separate branch of philosophy, it has a significant connection with metaphysics. Epistemology deals with the study of knowledge, its scope, sources, and limits. Metaphysics and epistemology often intersect when considering questions about the nature of reality and what we can know about it.

St. Thomas Aquinas integrated Aristotelian metaphysics with Christian theology. His works, particularly “Summa Theologica,” synthesized faith and reason and explored metaphysical concepts like the existence of God, the nature of the soul, and the relationship between faith and reason.
Philosophy of Mind: The Nature of Consciousness and Mental Phenomena
The philosophy of mind is a key aspect of metaphysics that explores the nature of consciousness, mental phenomena, and the mind-body relationship. Philosophers in this area ask questions like:
- What is consciousness?
- How does the mind interact with the physical body?
- Is the mind reducible to physical processes or does it have distinct properties?

Immanuel Kant introduced the idea of transcendental idealism, arguing that the mind plays an active role in shaping our perception of reality. He distinguished between phenomena (the world as we perceive it) and noumena (the world as it is in itself), challenging traditional metaphysical notions of objective reality.